A Linux distribution (often abbreviated as distro) is an operating system made from a software collection, which is based upon the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices (and personal computers.
A typical Linux distribution comprises a Linux kernel, GNU tools and libraries, additional software, documentation, a window system (the most common being the X Window System), a window manager, and a desktop environment. Most of the included software is free and open-source software made available both as compiled binaries and in source code form, allowing modifications to the original software.
Below you will find some of the Best Linux Distributions for 2017.
Read Also-
15 Linux Markdown Editors You Can’t Miss
1. Open Network Linux
Open Network Linux is a Linux distribution for “bare metal” switches, that is, network forwarding devices built from commodity components. ONL uses ONIE to install onto on-board flash memory.
Open Network Linux supports multiple switch fabric APIs including: OF-DPA, OpenNSL and SAI. Specific information about hardware support for the different APIs can be found in the HCL.
Open Network Linux is compatible with most forwarding agents including: Quagga, BIRD, Facebook FBOSS and Azure SONiC.
2. SemicodeOS
SemicodeOS is a Linux distribution especially built for programmers and web developers. Includes Most of Popular Programming Languages Compilers,top Editors and best Integrated Development Environments.
All you need to do after installing the Distro is to open your favourite code editor don’t worry it will be already pre-installed and start coding immediately.
3. VeltOS
VeltOS runs our very own Graphene Desktop, a simple interface designed to stay out of the way while still giving you quick access to all your applications and settings. Graphene is based on Google’s material design standards, and uses the Paper theme designed by Sam Hewitt.
VOS is based off Arch Linux especially because of its lightweight and rolling release nature and it is particularly known for its versatility, simplicity and cutting edge software. Arch provides its own software via the Pacman Package Manager and due to its rolling release model, you will always get the latest security updates and software packages.
4. Enchantment OS

Enchantment OS is a Linux distribution, tailored for ease of use, reliability and performance. It makes stable, secure Linux software goodness more accessible to nongeeky consumers and small business owners. Based on interviews and user trials with more than 200 real-world consumers from California to Florida, Enchantment OS has more of the features and apps that consumers need and less of the shiny nerdy stuff that they don’t.
Enchantment OS offers surprising performance on old and new PC hardware– even when booted from USB flash drives. It features a familiar desktop layout and a prominent app Menu button in the lower left corner. Enchantment is accompanied by my consumer-friendly user book.
5. Korora
Korora was born out of a desire to make Linux easier for new users, while still being useful for experts. Korora is a Fedora Remix, meaning it ships packages from the default Fedora repositories but also a number of other packages (often ones that Fedora cannot ship directly). We also make changes to the default system, whereas Fedora generally sticks to upstream. For new users, Fedora can be tricky because it doesn’t include many of the extras that users often need, things like media codecs and some proprietary software. This is one area where Korora can help.
Korora includes a tool called Pharlap for simple installation of third party drivers such as those for NVIDIA graphics cards and certain wireless devices.
Korora also comes with all the development tools and kernel headers you need to easily install out of tree kernel modules, such as those required by VirtualBox. These modules are automatically built when you get a new kernel update thanks to Dynamic Kernel Module Support.
6. Escuelas Linux
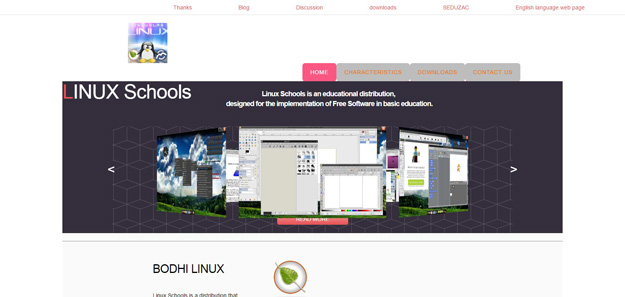
Escuelas Linux is a Bodhi Linux-based distribution that is built for elementary and high school education and includes out of the box a wide variety of educational software. Regardless of its Spanish name, it provides full English support as well.
Other distinguishing features of Escuelas Linux are a lightweight desktop environment and low-memory and storage requirements. According to the official website, it can work perfectly fine with as low as 300 MB of RAM and 20 GB of available hard disk space.
7. Antergos
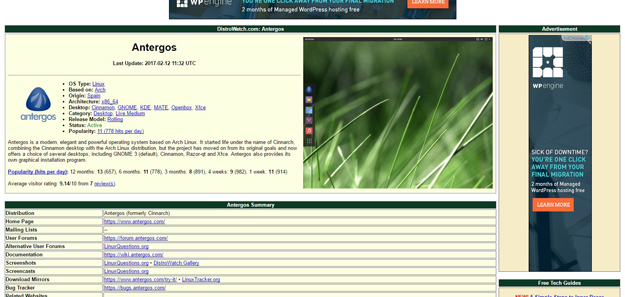
Antergos is a modern, elegant and powerful operating system based on Arch Linux. It started life under the name of Cinnarch, combining the Cinnamon desktop with the Arch Linux distribution, but the project has moved on from its original goals and now offers a choice of several desktops, including GNOME 3 (default), Cinnamon, Razor-qt and Xfce. Antergos also provides its own graphical installation program.
8. OviOS
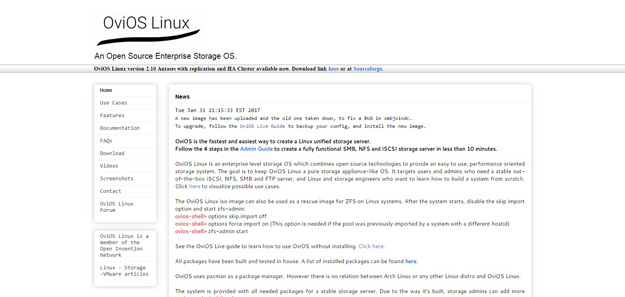
OviOS Linux is an enterprise level storage OS which combines open source technologies to provide an easy to use, performance oriented storage system. The goal is to keep OviOS Linux a pure storage appliance-like OS. It targets users and admins who need a stable out-of-the-box iSCSI, NFS, SMB and FTP server, and Linux and storage engineers who want to learn how to build a system from scratch.
OviOS uses pacman as a package manager. However there is no relation between Arch Linux or any other Linux distro and OviOS Linux.
The system is provided with all needed packages for a stable storage server. Due to the way it’s built, storage admins can add more packages, by building from source.
With OviOS Linux the user has complete control over how the system should work, what extra packages are needed and what services should run.
9. KDE neon
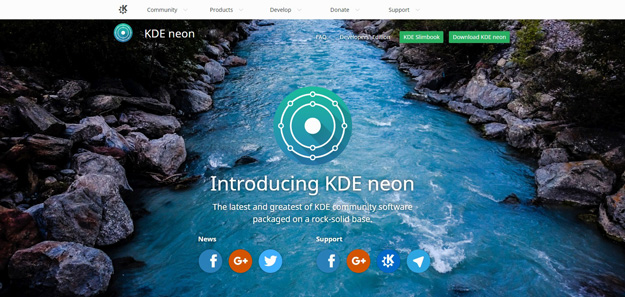
KDE neon is a Ubuntu-based Linux distribution and live DVD featuring the latest KDE Plasma desktop and other KDE community software. Besides the installable DVD image, the project provides a rapidly-evolving software repository with all the latest KDE software. Two editions of the product are available – a “User” edition, designed for those interested in checking out the latest KDE software as it gets released, and a “Developer’s” edition, created as a platform for testing cutting-edge KDE applications.
10. Solus
Solus is a Linux distribution built from scratch. It uses a forked version of the PiSi package manager, maintained as “eopkg” within Solus, and a custom desktop environment called “Budgie”, developed in-house. The Budgie desktop, which can be set to emulate the look and feel of the GNOME 2 desktop, is tightly integrated with the GNOME stack. The distribution is available for 64-bit computers only.
11. Ubuntu
Ubuntu is a complete desktop Linux operating system, freely available with both community and professional support. The Ubuntu community is built on the ideas enshrined in the Ubuntu Manifesto: that software should be available free of charge, that software tools should be usable by people in their local language and despite any disabilities, and that people should have the freedom to customise and alter their software in whatever way they see fit. “Ubuntu” is an ancient African word, meaning “humanity to others”. The Ubuntu distribution brings the spirit of Ubuntu to the software world.




